Key Takeaways
- Kernel-level anti-cheat gives deep access to monitor and control how software interacts with hardware, offering strong protection against cheats.
- ESEA and Vanguard are notable examples of kernel-level anti-cheat systems that have faced issues like a bitcoin miner and blue screen errors.
- Using kernel-level anti-cheat poses risks like system instability and conflicts with other software, with potential for catastrophic failures if updates go wrong.
If you're engaged in any of the competitive gaming landscape, then you've probably heard of kernel-level anti-cheat. It's an exceedingly controversial mechanism used to curb cheating In online games, but the trade-offs required for it aren't necessarily worth it. Not only are you giving an incredible amount of access to your computer to a games company, but the level of privilege that it runs at means that any bug or other problem introduced can cause your computer to blue screen or even fail to boot.
Related
DMA and AI are the next frontier of online cheating, but Riot has a plan
We spoke to Nick Peterson, Principal Software Engineer of Anti-Cheat, and Phillip Koskinas, Director and Head of Anti-Cheat of Riot.
What is kernel-level anti-cheat?
It runs at a privileged level

Kernel-level anti-cheat systems work directly at the core of a computer’s operating system, giving them deep access to monitor and control how software interacts with the hardware. This allows them to effectively detect and block cheats that attempt to manipulate game code or memory, offering stronger protection than traditional anti-cheat methods. This gives it the ability to spot cheats that utilize Direct Memory Access and other unique methods.
However, because these systems operate with such high-level access, they also pose significant risks. If there’s a flaw in the anti-cheat software, it could potentially compromise the entire computer, raising concerns about security and privacy. Additionally, this deep integration can sometimes cause conflicts with other software, leading to system instability.
These anti-cheats tend to be loaded as a driver, meaning that they operate with an incredible level of privilege on your computer. When a kernel-level anti-cheat driver is loaded, it runs with the same high-level permissions as the operating system itself, allowing it to oversee all other drivers, processes, and memory allocations on the system. This means it can detect unauthorized modifications or injections into a process' memory, except by running at such a privileged level, the anti-cheat driver can intervene before any cheat software can take effect, effectively blocking or reporting suspicious activities in real time.
Related
Best gaming laptops in 2024
Take your gaming on the go with one of these great laptops
Kernel-level anti-cheat has a pretty rough history
ESEA and Vanguard are two you may have heard of

There are plenty of games out there that use kernel-level anti-cheat nowadays, and some of the biggest are Counter-Strike 2 (through third-party services), League of Legends, and Valorant. Years and years ago, the third-party matchmaking service ESEA in Counter-Strike used a kernel-level anti-cheat to protect its games from cheaters. To the company's credit, ESEA was the go-to anti-cheat for years that uncovered a major cheating scandal across a small number of professional players.
However, it hasn't been all good with ESEA. On April 13th in 2013, a bitcoin miner was added to the ESEA client, which was discovered on May 1st. ESEA agreed to a $1 million settlement a year later, and the company blamed a rogue employee for the distribution of the miner. While a bitcoin miner can run without kernel-level access on a Windows machine, hiding it inside of an anti-cheat makes it harder to detect and protects it from being analyzed.
On top of that, a significantly more recent example came with the launch of the Vanguard anti-cheat in League of Legends. Vanguard has been used for a couple of years now in Valorant, and when it was eventually rolled out in League of Legends, a ton of users reported that their computers had started to face consistent blue screen of death errors. While Riot stated that a very small percentage of users had problems caused by Vanguard, users insisted that the problems only began after installing the anti-cheat, and some reported that the problems went away after removing it.
Related
How to move Valorant to an SSD
Improve your performance and get faster load times when you transfer Valorant to an SSD.
Is kernel-level anti-cheat needed?
it's a bit of a murky topic

Source: Battlestate Games
Looking back over the years, anti-cheat software versus cheat providers has been an incredibly long and drawn-out cat-and-mouse game. To be clear, any software on a Windows computer can be used to siphon information away and try to take control of your computer, and whether or not it runs at kernel level doesn't change that. For example, a kernel-level anti-cheat can access your webcam and see your screen, but so can any software that runs on your computer, too.
To illustrate the point, there is anti-cheat software still in use that hooks into your game (not at the kernel level) and takes screenshots every second for analysis. One popular free anti-cheat used for tournaments is called MOSS, and it will give you a ZIP file when you close your game that you can then hand over to the tournament operator. It's still somewhat invasive, but significantly less so than an anti-cheat that runs as a driver when you start your computer.
However, there's an argument to be made that the ever-growing arms race between cheat developers and anti-cheat developers is simply going to continue escalating. Nowadays, sophisticated cheats are also built as drivers for Windows, and they've been known in the past to use spoofed driver signatures so that they can pass driver signature verification. These kinds of tactics make it significantly harder to detect them, and why game developers feel that the natural evolution of anti-cheat software is to use these kernel-level anti-cheats.
One bad update can render millions of computers unusable
See: Crowdstrike
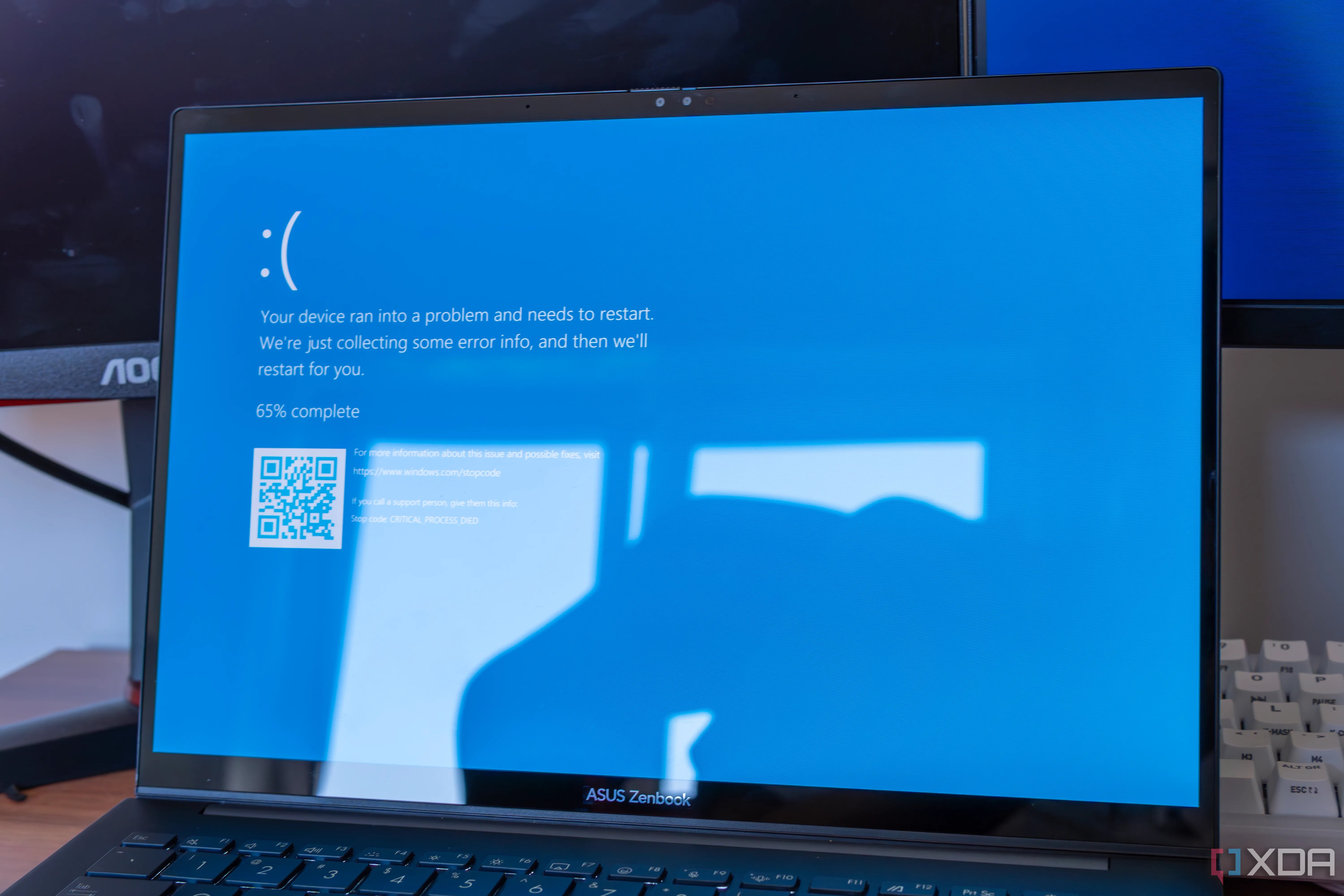
Here's the problem: when you have an anti-cheat running on millions of computers worldwide that runs when the system runs, there's a lot of control being handed over to the computer that makes the anti-cheat. In the case of Vanguard, one bad update would see computers around the world fail to boot. Imagine if an update went out by mistake with an untested change that crashed computers. That's basically what happened with CrowdStrike, a company that makes security solutions for enterprise consumers. Do you really think a gaming company wouldn't be capable of making a similarly colossal mistake?
Make no mistake, millions of people use their computers for gaming across the globe, and any update that would go out that could cause damage would cause damage on a similar scale to what happened with CrowdStrike. The issue is that users who don't know how to fix tech problems like these by themselves won't be able to get any help from the tech support afforded to big companies that were affected.
However, the damage that would be done would make it a true tech disaster that rivals some of the biggest to have ever happened. The difference would be that consumers are affected, not enterprise, but otherwise, the amount of damage done would still be incredible. Not only that, anti-cheat software could be vulnerable to malware, and could be a deeply privileged vector for an attacker to gain access to a machine.
As it stands, these companies test and deploy anti-cheat software on their own machines, which should avoid the vast majority of potential problems, but then again, you would think the same of what happened with CrowdStrike, too. Plus, given that we've already seen what has happened in the past with both ESEA and Vanguard, it's not impossible that other problems can rear their heads on top of that.
Related
Forget CrowdStrike - Here are 5 companies you've never heard of that the world relies on
A lot of computational control is consolidated across very few companies, and here are five you've never heard of.
2
- Software and Services
- Windows 11: Everything you need to know
- Gaming
Your changes have been saved
Email is sent
Email has already been sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Manage Your List
Follow
Followed
Follow with Notifications
Follow
Unfollow
Readers like you help support XDA. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read More.